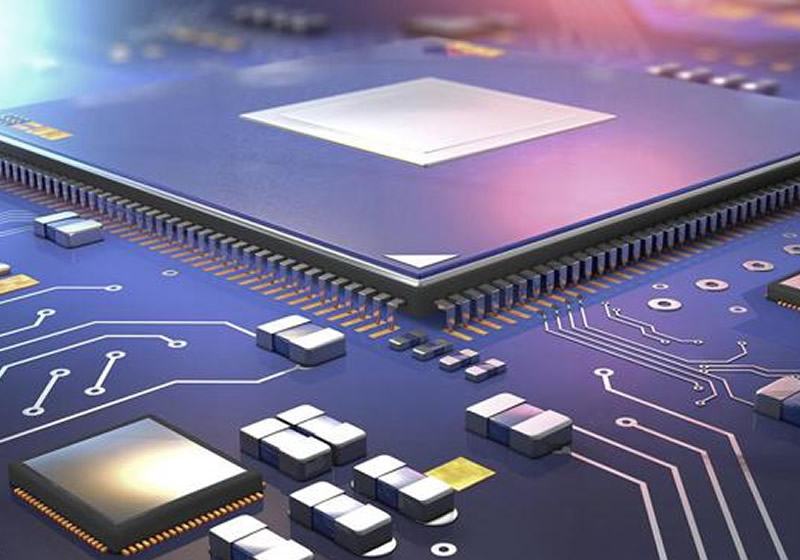
In digital circuits, most transistors work in the on/off state.
The circuit that uses digital signals to perform arithmetic and logical operations on digital quantities is called a digital circuit, or a digital system. Due to its logical operation and processing functions, it is also known as a digital logic circuit. Modern digital circuits are constructed from several digital integrated devices made using semiconductor technology. Logic gates are the fundamental units of digital logic circuits.
Memory is a digital circuit used to store binary data. Overall, digital circuits can be divided into two categories: combinational logic circuits and sequential logic circuits. From the previous introduction, we have learned that digital circuits are based on binary digital logic, and their working signals are discrete digital signals. The electronic transistor in the circuit operates in a switching state, sometimes conducting and sometimes cutting off.
The materials used in digital integrated devices are mainly silicon materials, and compound semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide are also used in high-speed circuits. Logic gates are an important type of logic unit circuit in digital circuits. TTL logic gate circuits emerged early, and their technology has been continuously improved, still being one of the main basic logic devices to this day.
With the development of CMOS technology, the dominant position of TTL has been shaken and there is a trend of being replaced by CMOS devices. In recent years, the rapid progress of programmable logic devices (PLDs), especially field programmable gate array (FPGA), has opened up a new era in digital electronic technology. Not only is it large-scale, but it also combines hardware and software, making the functions of the devices more complete and flexible to use.


 Phone: 0755-84715624
Phone: 0755-84715624 Mobile: 18038109879
Mobile: 18038109879 Contact: He Yu
Contact: He Yu Email: sales01@aitaiwei.com
Email: sales01@aitaiwei.com website: www.aitaiwei.com
website: www.aitaiwei.com Address: Room 702, Maple Leaf Pavilion, Building C3, Fuhua Garden, Bantian Street, Longgang District, Shenzhen
Address: Room 702, Maple Leaf Pavilion, Building C3, Fuhua Garden, Bantian Street, Longgang District, Shenzhen